The SafeGuard Cyber Master Glossary
At SafeGuard Cyber, we understand the importance of staying ahead in a world where digital risks are constantly evolving.
Begin your transformation to secure and compliant communication. Share your information so we can connect.

Download PDF
This glossary is part of our commitment to empowering you with the knowledge and tools necessary for robust security and compliance protection. We have designed this guide to enhance your understanding and empower you to make informed decisions in safeguarding your digital environment.
Cybersecurity Threats and Attacks
Learn about various forms of digital threats and attacks, ranging from sophisticated phishing scams to advanced corporate espionage. Understanding these terms is vital for identifying potential risks and implementing effective security measures to protect your organization from malicious actors.
 Baiting
Baiting
Luring victims with the promise of goods or services to steal information or infect systems with malware.
 Big Game Hunting
Big Game Hunting
Targeting large organizations for significant financial gain through ransomware or other cyber attacks.
 Business Communications Compromise (BCC)
Business Communications Compromise (BCC)
Similar to Business Email Compromise ( BEC), but involves compromising legitimate business communication applications like Slack, Microsoft Teams, WhatsApp, Telegram in addition to email accounts for unauthorized transactions.
.png?width=81&height=81&name=Business%20Email%20Compromise%20(BEC).png) Business Email Compromise (BEC)
Business Email Compromise (BEC)
A sophisticated scam targeting businesses to transfer funds to the attacker's account.
 Corporate Espionage
Corporate Espionage
Spying is conducted for commercial purposes, often involving cyber tactics.
 Crypto-malware
Crypto-malware
A form of malware that encrypts files on a computer and demands a ransom in cryptocurrency.
 Doxware/Leakware
Doxware/Leakware
Malware that threatens to publish stolen information from a computer unless a ransom is paid.
 Extortion
Extortion
Threatening to harm a person or their reputation unless a demand (usually monetary) is met.
 Honey Trap
Honey Trap
A deceptive practice of using romantic or sexual attraction to extract information or concessions.
 Indicators of Attack
Indicators of Attack
Signs or activities suggesting a network or system is under cyber attack.
 Lockers
Lockers
A type of ransomware that locks users out of their operating systems, making it impossible to access their desktop and files.
 Pharming
Pharming
Redirecting users from legitimate websites to fraudulent ones for the purpose of extracting confidential data.
 Phishing
Phishing
A fraudulent attempt to obtain sensitive information by disguising as a trustworthy entity in electronic communication.
 Pretexting
Pretexting
The act of creating a fabricated scenario to steal a victim's personal information.
 Quid Pro Quo
Quid Pro Quo
Offering a benefit in exchange for information, often used in social engineering attacks.
 RaaS (Ransomware as a Service)
RaaS (Ransomware as a Service)
A business model where malware creators sell or rent ransomware to other criminals.
 Ransomware/Malware
Ransomware/Malware
Malicious software that encrypts a victim's data and demands payment for its release.
 Rogue Security Software
Rogue Security Software
Malware that tricks users into believing their computer is infected with a virus, then suggests downloading and paying for fake antivirus software.
 Scareware
Scareware
A type of malware designed to trick victims into buying and downloading unnecessary and potentially harmful software.
 Smishing
Smishing
SMS phishing, a form of phishing involving text messages.
 Social Engineering
Social Engineering
Manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information.
 Social Media Phishing
Social Media Phishing
Phishing attacks carried out through social media platforms.
 Spear Phishing
Spear Phishing
A more targeted form of phishing, where attackers focus on specific individuals or organizations.
 Vishing
Vishing
Voice phishing where fraud is committed using telephone calls.
 Watering Hole
Watering Hole
A cyber attack strategy where the attacker guesses or observes which websites an organization often uses and infects them with malware.
 Whaling
Whaling
A type of spear phishing targeting high-profile individuals like C-level executives.

Cybersecurity Solutions and Strategies
Examine an array of solutions and strategies employed to combat digital threats. This section covers everything from advanced AI technologies to comprehensive security models, offering insights into the tools and methodologies that fortify digital defenses.
%201.svg) Archiving
Archiving
Storing data securely for long-term retention and compliance purposes.
 Behavioral Analysis
Behavioral Analysis
Monitoring and analyzing user behavior to detect anomalies that may indicate security threats.
 Causal AI
Causal AI
Causal artificial intelligence (AI) identifies and utilizes cause-and-effect relationships to go beyond correlation-based predictive models and toward AI systems that can prescribe actions more effectively and act more autonomously. It includes different techniques, such as causal graphs and simulation, that help uncover causal relationships to improve decision making.
 Compliance
Compliance
Ensuring that organizational practices meet regulatory and legal requirements.
 Contextual AI
Contextual AI
Artificial intelligence that understands the context of data and user interactions for better threat detection.
 Contextual Analysis
Contextual Analysis
Examining the context surrounding data and events to identify security threats.
 Cross-Channel Event Correlation
Cross-Channel Event Correlation
Analyzing events across different communication channels to detect security incidents.
 Data Loss Protection (DLP)
Data Loss Protection (DLP)
Strategies and tools to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access or use of data.
 Deployment Model
Deployment Model
The method of implementing cybersecurity solutions in an organization.
 Generative AI
Generative AI
AI capable of generating new content, often used in cybersecurity to simulate attacks or predict threats.
 Illuminate Partner Program
Illuminate Partner Program
A partnership program by SafeGuard Cyber, focusing on enhancing cybersecurity measures.
 Impact Analysis
Impact Analysis
Assessing the potential consequences of identified cybersecurity threats.
%201.svg) Impersonation
Impersonation
Detecting and preventing attempts to mimic or assume the identity of legitimate users or entities.
 Integrated Cloud Communication Security
Integrated Cloud Communication Security
Security measures designed to protect cloud-based communication platforms.
 Integrated Cloud Email Security
Integrated Cloud Email Security
Protecting email communications within cloud environments from threats.
 LLMs (Large Language Models)
LLMs (Large Language Models)
Advanced AI models capable of understanding and generating human-like text.
 Magnitude of Impact
Magnitude of Impact
A metric used in cybersecurity to evaluate the potential severity and consequences of a security threat, aiding in prioritizing responses.
 Multilingual Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Multilingual Natural Language Processing (NLP)
AI technology that processes and understands multiple languages for security analysis.
 Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
AI's ability to understand and interpret human language.
 Ontological Architecture
Ontological Architecture
A framework for modeling data that defines the relationships between different entities.
 Remediation
Remediation
The process of fixing vulnerabilities or mitigating threats in a cybersecurity context.
%201.svg) SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS (Software as a Service)
A software distribution model where applications are hosted by a service provider and made available over the internet.
 Security
Security
Measures and strategies to protect digital information and IT infrastructure.
 Social Knowledge Graphs
Social Knowledge Graphs
Using network theory to understand and analyze social connections for threat detection.
 Unified Visibility
Unified Visibility
A comprehensive view of AI cloud communication activities to identify and manage threats.
 Vision and Voice
Vision and Voice
Community led by SafeGuard Cyber CMO, Lisa Hayashi with the goal of helping women ascend in the cybersecurity industry.
 XDR (Extended Detection and Response)
XDR (Extended Detection and Response)
A security solution that provides comprehensive threat detection and response across networks, endpoints, and clouds.
 Zero Trust
Zero Trust
A security model that requires strict identity verification for every person and device trying to access resources.

Compliance Terms
Compliance is a critical aspect of digital security, especially for organizations in regulated industries. Get clarity on terms related to regulatory requirements, policy governance, and risk management, ensuring your organization's digital practices align with legal standards.
 Archive Communications
Archive Communications
Securely storing digital communications, like emails and social media posts, to meet regulatory requirements.
 Automated Policy Supervision
Automated Policy Supervision
Providing comprehensive, automated policy supervision to address various compliance requirements.
 Automated Supervision
Automated Supervision
Using automated tools for monitoring digital communications to ensure policy and regulatory compliance.
 Compliance Automation
Compliance Automation
Automating processes and controls to ensure adherence to regulatory and legal requirements, especially in digital communications and social media.
 Compliance for Financial Services
Compliance for Financial Services
Ensuring digital communication strategies in finance comply with regulations like those from the SEC or FINRA.
 Compliance for Mobile Chat Communications
Compliance for Mobile Chat Communications
Applying compliance measures to mobile chat platforms to meet regulatory standards.
 Compliant Social Selling
Compliant Social Selling
Using social media for sales while adhering to regulatory and compliance standards.
 Modern Digital Compliance
Modern Digital Compliance
A contemporary approach to compliance, focusing on consistent policy supervision across digital channels.
 Multichannel Analysis and Archiving
Multichannel Analysis and Archiving
Archiving and analyzing content across digital channels in native formats for audit and litigation readiness.
 Policy-based Governance
Policy-based Governance
Implementing and enforcing policies governing digital communication tools to maintain industry compliance.
 Regulatory Risk Management
Regulatory Risk Management
Identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks from changes in laws and regulations, particularly in digital communications.
 Transparent Machine Learning
Transparent Machine Learning
Utilizing machine learning to reduce false positives in compliance monitoring and supervision.
 Unified Visibility for Scale
Unified Visibility for Scale
Ensuring security and compliance for business needs across various languages and channels.

Data and Analysis Techniques
Data is at the heart of digital security. This category sheds light on the analytical techniques used to interpret and leverage data for enhanced security, from behavior analytics to machine learning.
 Behavior Analytics
Behavior Analytics
Analyzing data about how users behave across cloud communication channels to detect potential security threats.
 Machine Learning
Machine Learning
A type of AI that allows software applications to become more accurate at predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed to do so.
 Metadata Traits
Metadata Traits
Characteristics and data that describe other data, providing context or summarizing basic information.
 Semantic Analysis
Semantic Analysis
The process of understanding the meaning and interpretation of words and sentences in context.
 Social Graph Analysis
Social Graph Analysis
Examining the networks of social relationships to understand behaviors and trends.

Insider Threats and Data Protection
Understanding the internal risks to your organization is as important as external threats. This section focuses on the challenges of insider threats and the importance of robust data privacy measures.
 Credential Theft
Credential Theft
The unauthorized acquisition of usernames and passwords to gain access to systems and data.
 Data Privacy
Data Privacy
Protecting personal or sensitive information from unauthorized access and ensuring its proper handling.
 Insider Threats
Insider Threats
Security risks that originate from within an organization, often by employees or former employees.

Marketing and Sales
In the digital age, marketing and sales strategies are increasingly intertwined with cybersecurity and compliance. Get insights into how digital tools and platforms can be leveraged safely and effectively in these domains.
 Collaboration
Collaboration
Working jointly with others, often using digital tools, to achieve business objectives.
 CRM Free Text
CRM Free Text
Unstructured text data in a Customer Relationship Management system, often analyzed for insights into customer interactions.
 Mobile Messaging
Mobile Messaging
Communicating with customers or prospects through mobile text messaging platforms.
 Social Selling
Social Selling
Using social media platforms to interact directly with prospects, providing value by answering questions and offering thoughtful content.

The Changing Nature of Work
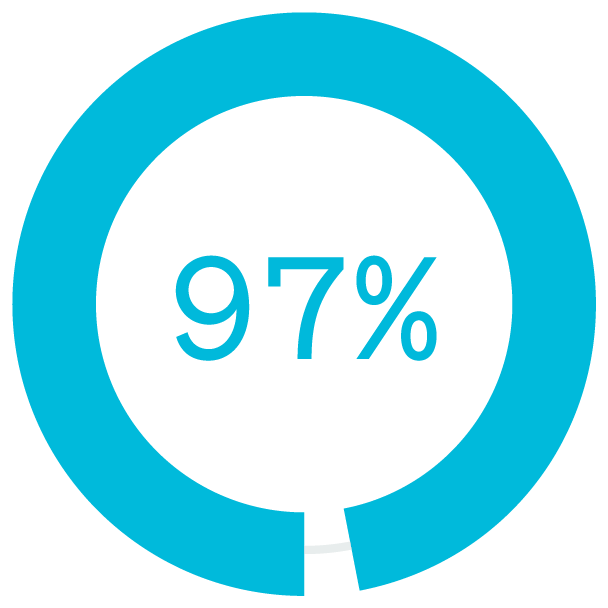
of North American office workers worked from home more than one day per week
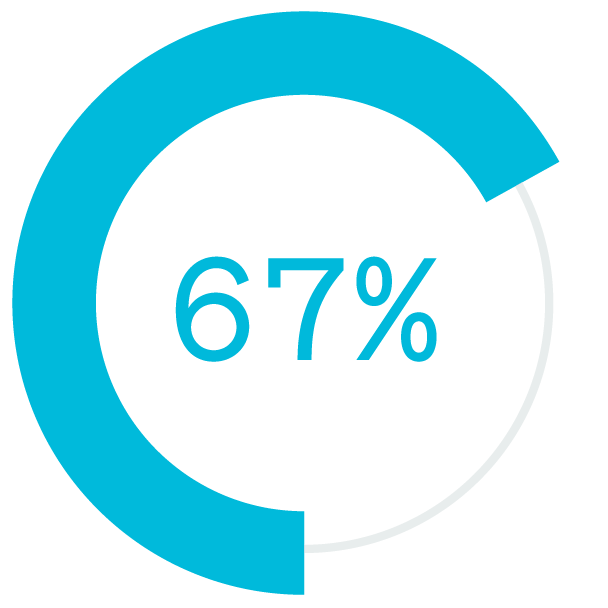
had not worked remotely prior to COVID-19
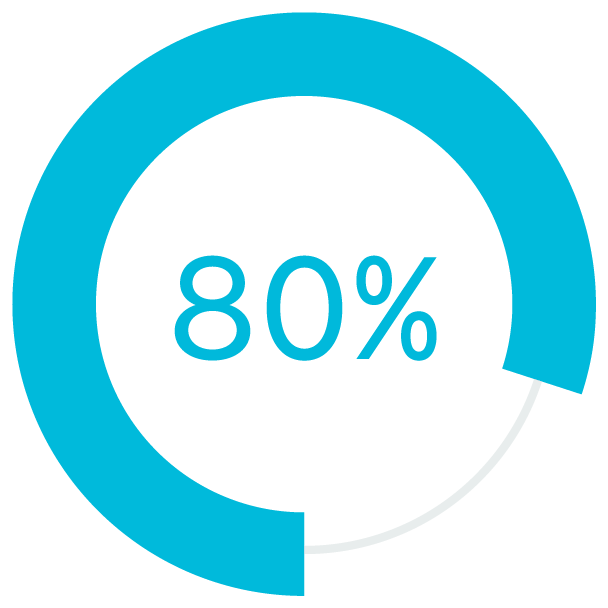
of workers prefer a hybrid work environment
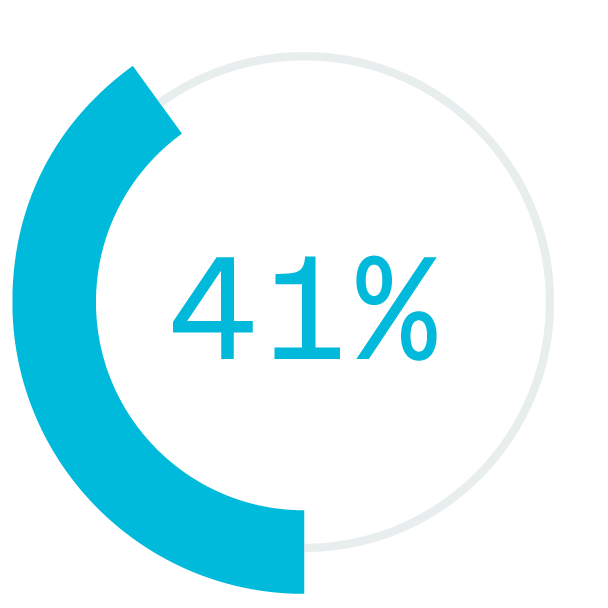
lower absenteeism
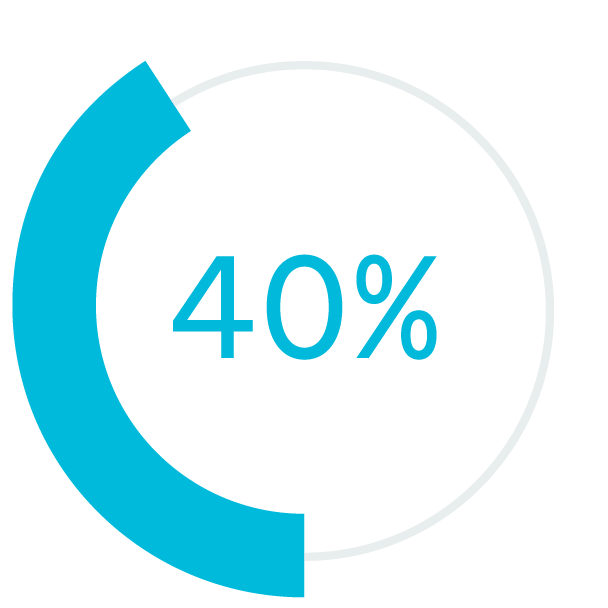
fewer quality defect
higher profitability
Something Powerful
Tell The Reader More
The headline and subheader tells us what you're offering, and the form header closes the deal. Over here you can explain why your offer is so great it's worth filling out a form for.
Remember:
- Bullets are great
- For spelling out benefits and
- Turning visitors into leads.
lower absenteeism
fewer quality defect
higher profitability
Text
Flexible work environments require access to on-premises systems and data, and therefore most enterprises rely on employees using a VPN. However, organizations can’t trust that workers will always use these secure channels. If an employee is using a mobile phone, he or she might forget to use the VPN and employ an unsecured wireless network instead, exposing corporate systems and data to risk.
During the pandemic, threat actors realized that insecure home networks and a lack of security controls typically found on corporate networks could work to their benefit. The World Economic Forum estimates cyber attacks jumped 238% globally between February and April 2020.
Technical Requirements
Secure Infrastructures
Flexible work environments require access to on-premises systems and data, and therefore most enterprises rely on employees using a VPN. However, organizations can’t trust that workers will always use these secure channels. If an employee is using a mobile phone, he or she might forget to use the VPN and employ an unsecured wireless network instead, exposing corporate systems and data to risk.
During the pandemic, threat actors realized that insecure home networks and a lack of security controls typically found on corporate networks could work to their benefit. The World Economic Forum estimates cyber attacks jumped 238% globally between February and April 2020.
Technical Requirements
Secure Infrastructures
Flexible work environments require access to on-premises systems and data, and therefore most enterprises rely on employees using a VPN. However, organizations can’t trust that workers will always use these secure channels. If an employee is using a mobile phone, he or she might forget to use the VPN and employ an unsecured wireless network instead, exposing corporate systems and data to risk.
During the pandemic, threat actors realized that insecure home networks and a lack of security controls typically found on corporate networks could work to their benefit. The World Economic Forum estimates cyber attacks jumped 238% globally between February and April 2020.
NEW ROLE OF THE CISO
Over 80% of security professionals believe social media, mobile messaging, or collaboration apps present medium to high risks to their organization.
SafeGuardCyber Survey April, 2019
Secure Infrastructures
Flexible work environments require access to on-premises systems and data, and therefore most enterprises rely on employees using a VPN. However, organizations can’t trust that workers will always use these secure channels. If an employee is using a mobile phone, he or she might forget to use the VPN and employ an unsecured wireless network instead, exposing corporate systems and data to risk.
During the pandemic, threat actors realized that insecure home networks and a lack of security controls typically found on corporate networks could work to their benefit. The World Economic Forum estimates cyber attacks jumped 238% globally between February and April 2020.
Text
Flexible work environments require access to on-premises systems and data, and therefore most enterprises rely on employees using a VPN. However, organizations can’t trust that workers will always use these secure channels. If an employee is using a mobile phone, he or she might forget to use the VPN and employ an unsecured wireless network instead, exposing corporate systems and data to risk.
During the pandemic, threat actors realized that insecure home networks and a lack of security controls typically found on corporate networks could work to their benefit. The World Economic Forum estimates cyber attacks jumped 238% globally between February and April 2020.
Organizations also increasingly rely on cloud-based collaboration platforms and personal communications technologies to connect teams across regions and time zones.
With the sudden onset of the pandemic, many organizations abruptly switched to remote work and found themselves having to allow technologies like MS Teams, Slack, Zoom and Webex on a scale they were uncomfortable permitting earlier. At the time, many IT leaders believed these solutions would be temporary and they’d quickly go back to "normal."
Now, more than a year later, not only are organizations continuing to use these technologies, but they’re doubling down. Yet, they still have no way to keep these systems secure from third-party risks. For example, a recent attack against EA Games involved infiltrating the company’s Slack instance and launching a fileless social engineering scheme to gain access to the network, resulting in the theft and exfiltration of highly-valuable intellectual property.
Similarly, IT once viewed communications solutions like WhatsApp and WeChat as personal apps. Because corporate teams had zero visibility into them, they would not allow employees to do business on them. But in some critical emerging markets, only a small percentage of people use email. Most use mobile chat applications like WhatsApp. It has become a business imperative to use the local technology.
New Security Challenges
These collaboration and communications tools present significant data governance and security challenges for large organizations. In a survey by SafeGuard Cyber:
- 78% of cybersecurity leaders express an inability to protect all communication channels and digital assets6
- 46% say collaboration tools represent the biggest security challenge
- 1 in 3 say their biggest challenge is mobile chat apps, WhatsApp, WeChat, Telegram
- 1 in 5 say their biggest challenge is Video meetings (Zoom, Webex, etc. )
Hybrid work environments will only increase the challenges. As employee devices and laptops move onto the corporate network and then back home where they can be exposed to hackers and more easily infected with malware and ransomware, it will be difficult for security teams to protect employees from threats, detect and respond to insider threats, or stop malware and ransomware.

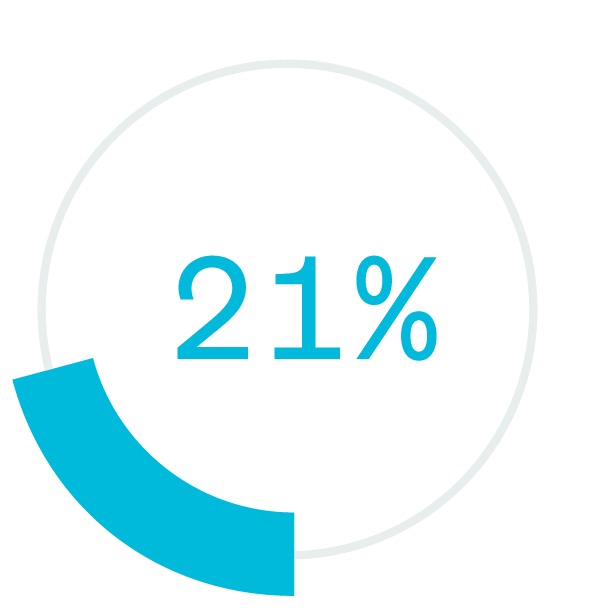
Only 20% of security professionals feel confident they are effectively mitigating the digital risks from social media, messaging and collaboration apps.
SafeGuardCyber Survey April, 2019
SafeGuardCyber Survey April, 2019
SafeGuardCyber Survey April, 2019
SafeGuardCyber Survey April, 2019
Lorem ipsum dolor
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Nulla urna massa, maximus at neque vel, mollis efficitur.
Benefits
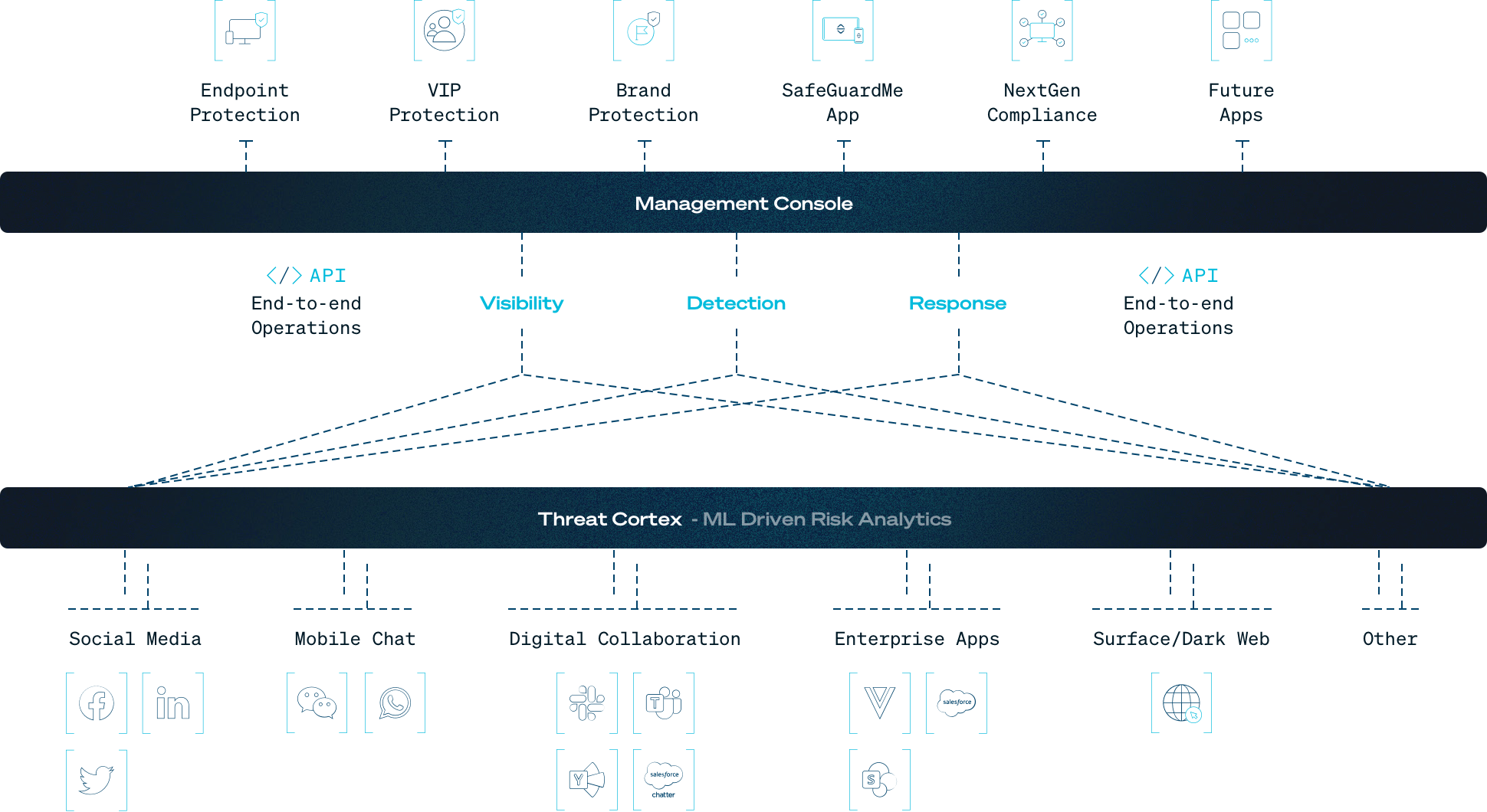
With SafeGuard Cyber’s agentless architecture, organizations benefit from:
Gain unprecedented visibility to respond to internal and external threats in hard-to-see places like direct messages and group channels. Reduce detection and response times in the cloud infrastructure where work gets done.
Be up and running in hours not days. Organizations no longer have to configure agents.
Connect our agentless security platform into your existing cyber defense systems, feeding event data and telemetry into your EDR and SIEM solutions.
Secure Human Connections
Ready to see how SafeGuard Cyber secures modern communication apps wherever they exist?
Expert Insights on Cloud App Risks
Stay up-to-date on the latest insider threats, ransomware, and third-party vulnerabilities.

